Toys play a pivotal role in shaping the experiences and development of children worldwide. While toys bring joy and imagination to young minds, it is crucial to ensure that they are safe and meet stringent quality standards. This is where toy safety standards and international requirements come into play, safeguarding children’s well-being and promoting responsible manufacturing practices.
The Importance of Toy Safety Standards:
Toy safety standards serve as a protective shield, ensuring that toys do not pose hazards to children. These standards encompass guidelines and regulations that manufacturers, distributors, and retailers must adhere to, from the design phase to the point of sale. The primary objective is to minimize risks related to choking, sharp edges, chemical exposure, and other potential dangers.
International Harmonization:
In an interconnected world, toys are often produced in one country and sold in another. This is where international harmonization becomes critical. Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Consumer Product Safety Caucus (ICPSC) collaborate to establish uniform toy safety requirements across borders. This not only streamlines the manufacturing process but also ensures that children everywhere can enjoy safe and high-quality toys.
Key Components of Toy Safety Standards:
1. Physical Safety: Toy safety standards address physical aspects such as size, shape, and materials. Small parts that could be swallowed, sharp edges, and the durability of components are all evaluated to prevent accidents.
2. Chemical Safety: Toxic substances like lead, phthalates, and other harmful chemicals are strictly regulated. Toys must undergo testing to ensure they meet permissible limits, safeguarding children from potential health risks.
3. Mechanical and Electrical Safety: Battery-operated toys and those with moving parts undergo thorough testing to prevent pinching, entrapment, or electrical hazards. These standards help prevent injuries related to mechanical failures or electrical malfunctions.
4. Flammability: Toys need to be fire-resistant to prevent the risk of ignition, especially in cases where children’s curiosity might lead to them being near open flames.
The Anatomy of Toy Safety Standards:
1. Age Appropriateness: Toy safety standards take into account the developmental stages of children. Toys must be designed with age-appropriate features that challenge and engage without presenting undue risk. From newborns to teenagers, these standards cater to the specific needs of each age group.
2. Testing and Certification: Rigorous testing is the cornerstone of safety standards. Toys undergo various assessments, including mechanical and chemical tests, to ensure they are free from hazards. Independent testing bodies evaluate these toys, awarding certifications that denote compliance with safety guidelines.
3. Small Parts and Choking Hazards: The potential for choking is a significant concern, especially for younger children. Standards dictate the maximum size of parts to prevent accidental swallowing and choking incidents.
4. Noise and Hearing Safety: Toys that produce sounds are evaluated to ensure that the volume levels are safe for delicate young ears. Prolonged exposure to loud sounds can potentially harm a child’s hearing.
5. Art and Craft Supplies: Even beyond conventional toys, art and craft supplies aimed at children are scrutinized. Crayons, paints, and other materials are checked for toxic elements that might pose health risks.
6. Online and Digital Safety: In the digital age, interactive toys and apps are subject to safety standards. These standards encompass privacy, age-appropriateness, and protection against cyber threats.
Global Collaboration for Safety:
1. International Standards Organizations: Entities like ISO, ASTM International, and IEC contribute to the establishment of consistent safety standards across the globe. Their work involves gathering expertise from various sectors to develop comprehensive guidelines.
2. The Role of Governments: Many governments have regulatory bodies responsible for enforcing toy safety standards within their borders. These agencies often conduct inspections, issue recalls when necessary, and communicate safety alerts to the public.
3. Continuous Evolution: Toy safety standards are not static; they evolve alongside technological advancements and emerging risks. This adaptability ensures that safety remains a priority even as new types of toys enter the market.
Empowering Parents and Guardians:
Understanding safety standards empowers parents and guardians to make informed decisions when selecting toys. Recognizing safety certification marks and reading product labels help ensure that toys meet the necessary criteria.
Certification and Compliance:
Before toys can be distributed and sold, they must be certified as compliant with the appropriate safety standards. Regulatory bodies and independent third-party testing laboratories assess toys to ensure they meet safety criteria. Certifications provide parents, guardians, and retailers with the confidence that the toys have undergone rigorous testing and are safe for children to use.
Ongoing Surveillance:
The responsibility for toy safety doesn’t end after the manufacturing process. Regular monitoring and market surveillance are essential to identify potential risks associated with toys already in circulation. If a safety issue arises, quick action can be taken to recall the products and rectify the situation.
Consumer Awareness:
Parents and guardians play a vital role in ensuring toy safety. By staying informed about safety standards, checking for certification labels, and reporting any issues, they actively contribute to a safer environment for children.
The Importance of Toy Safety Standards:
1. Preserving Innocence: Childhood is a time of wonder, and toys are a gateway to imagination. Safety standards ensure that this enchanting period remains untainted by preventable accidents and hazards.
2. Guardians of Well-being: Children are inherently curious, and their exploration often involves tasting, touching, and interacting with toys. Safety standards prevent toxic substances and choking hazards from turning these natural inclinations into dangers.
3. Building Trust: Manufacturers that adhere to safety standards demonstrate their commitment to children’s welfare. Parents and guardians can confidently select toys knowing that they meet rigorous criteria for safety.
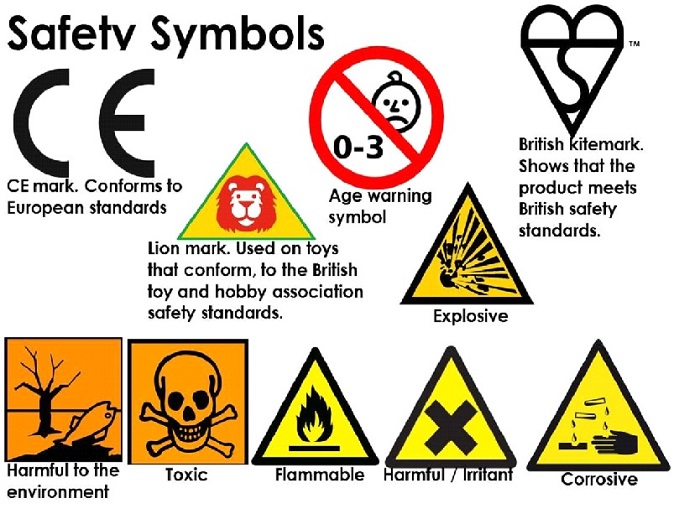
Overview of Toy Safety Standards:
1. Materials and Components: From the paint used on wooden toys to the plastic in action figures, materials must be free from harmful chemicals and toxins. Standards dictate the permissible levels of these substances.
2. Design and Construction: Toys must be designed to withstand normal wear and tear without presenting sharp edges or small parts that could break off. Sturdy construction enhances both the longevity and safety of toys.
3. Age Appropriateness: Safety standards are attuned to the developmental stages of children. Toys must not only cater to these stages but also ensure that components like buttons, batteries, or strings are safe for a child’s age group.
Understanding International Toy Safety Requirements:
1. Global Harmonization: International toy safety standards work towards harmonizing regulations across countries. This enables manufacturers to produce toys that can be sold worldwide without the need for drastic design alterations.
2. Cross-Border Confidence: As toys are manufactured in one corner of the world and enjoyed in another, international standards foster confidence that the toy adheres to safety criteria, regardless of its origin.
Challenges in Meeting Toy Safety Standards and Requirements:
1. Complexity of Supply Chains: Toy production often involves multiple suppliers and subcontractors, making it challenging to ensure that every component meets safety standards.
2. Emerging Technologies: As toys become more interactive and technologically advanced, ensuring the safety of integrated electronics and digital components becomes more intricate.
3. Cost and Profit Margin: Implementing safety measures might increase production costs, potentially impacting profit margins. Balancing safety with affordability is a delicate equation.
4. Rapid Product Development: In a dynamic market, rapid product development can sometimes lead to shortcuts in safety testing. Striking a balance between innovation and safety remains a hurdle.

Conclusion:
Safe Adventures, Bright Futures:
The allure of toys lies not only in their colors and shapes but in the promise of discovery and growth. Toy safety standards and international requirements serve as companions on this journey, ensuring that every adventure is free from unnecessary risk. As we celebrate the joy of play, let us also celebrate the dedication of manufacturers, regulators, and caregivers who unite to make this joy safe and enduring. In the heart of every toy lies a universe of possibilities, and it is our collective responsibility to make this universe a haven of safety and wonder for generations to come.



